THE ONGOING TRADE WAR BETWEEN THE U.S., CHINA, AND EUROPE WILL CAUSE WORLD TRADE TO CONTINUE TO SLOW.
FROM THE BLEACHERS, VOL. 20
MARKET UPDATE
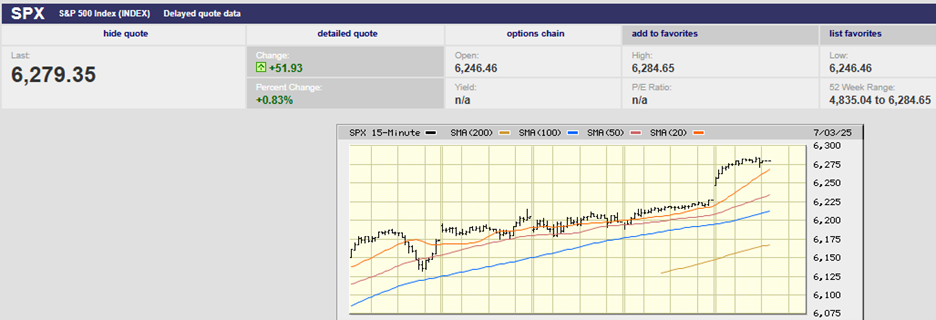
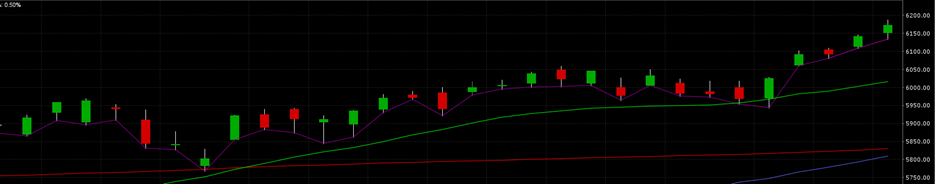
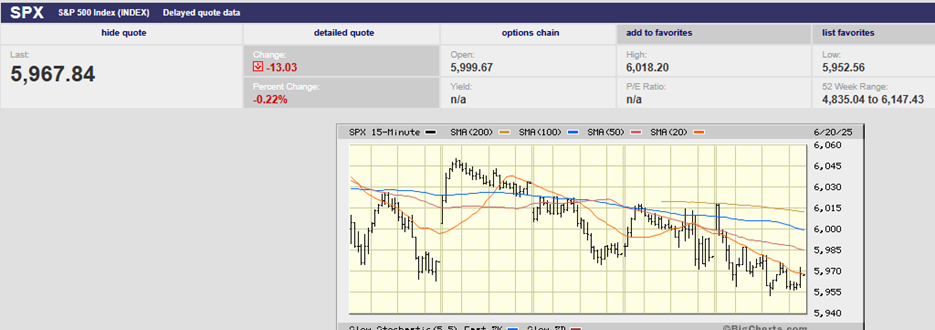
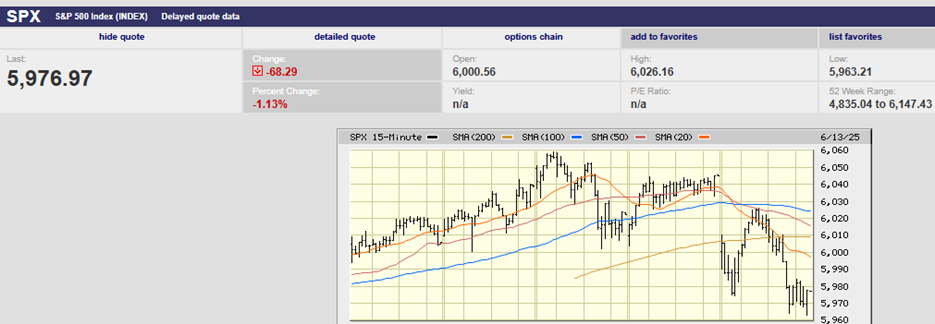
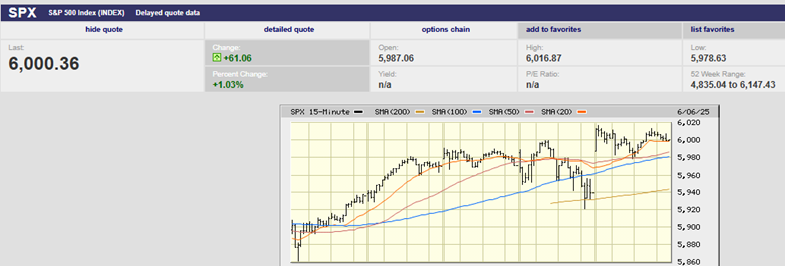
The S&P 500 fell 0.8% on the week, finishing at 2859.53. The index fell 2.5% on Monday, as traders did indeed test the downside, and is now down 3% on the month. The China trade talks continue to be the one thing the market is supposedly focused on now, according to most of the talking heads on TV and radio. Regardless, the index bounced off 2800 before recovering lost ground most of the rest of the week. It did manage to finish back above the 50-day moving average on Thursday, but couldn’t hold on gapping down Friday below the 50-day, rallying above during the day only to sell-off again and close below the 50-day for the week (creating an inverted cross in the process). Expect the market to test the downside on Monday barring any major positive fundamental news over the weekend.
There wasn’t much U.S. economic data out last week, but one notable reading was a 15-year high in Consumer Confidence, which registered 102.4 in May, up from 97.2 in April. Also, a survey of U.S. economic conditions rose for the 3rd straight month in April, an increase of 0.2% over March. The Conference Board survey points to economic growth slowing to 2.0% by the end of 2019. The current expansion will enter its 11th year in July, making it the longest economic expansion in U.S. history.
As for the China Trade War – the foreign exchange (forex) market is reacting with the yuan testing the 7.0 level (7.0 Yuan per dollar). It finished Friday at 6.95. According to forex experts, China has defended the 7.0 level for years turning it into a psychologically important level and one to watch in the ongoing trade war. There is increasing speculation that the Chinese may allow their currency to drop against the dollar to offset at least some of the impact of the tariffs currently being imposed on them by the U.S. A depreciation of the yuan would make Chinese exports to the U.S. cheaper.
There is a consensus among economic experts that the ongoing trade war between the U.S., China, and Europe will cause world trade to continue to slow. In fact, “world trade shrank by 0.3 percent in the fourth quarter of 2018 and is likely to grow by 2.6 percent this year, below a previous forecast of 3.7 percent,” the World Trade Organization said in early April, according to Reuters. Another point to keep in mind is that Europe’s current production surplus is far larger than the Chinese production surplus. Measured in dollars, Italy’s excess production in 2018 was larger than China’s, according to Barron’s. Excess output from the 19 members of the euro area is now worth about 0.6% of world production, while Chinese excess output is currently just 0.1%. Of course, excess output, output that isn’t being consumed at home, results in increased exports to U.S. shores since we are historically the world’s consumer of last resort. Given Trump’s obsession with trade deficits, it’s unlikely that he will drop confrontational trade policy off his agenda anytime soon.
All of which means that there is plenty of opportunity for the major trading blocks to further damage the world economy with ongoing tariff wars that will eventually feed into the financial markets in a more lasting manner.
INVESTING – INTEREST RATES, CAPITAL FLOWS, EXCHANGE RATES AND THE STOCK MARKET
We live in a world economy whether we like it or not; goods, services, and capital flow around the world seeking the best prices and highest returns on investment. Falling U.S. interest rates cause capital to flow overseas in search of a higher return, which in turn causes the dollar to fall in value relative to other currencies as the supply of dollars on the international stage increases. The reverse is true when U.S. interest rates rise; capital flows out of foreign markets back into the U.S. causing interest rates overseas to rise, economies to slow, and stock markets to fall.
It is the adjustment in real exchange rates that prevents trade policy from actually impacting the trade balance. Placing a tariff on Chinese goods reduces the amount of Chinese imports, which increases our net exports temporarily. However, the increase in net exports creates increased demand for dollars, which causes the dollar to appreciate against other currencies. As the dollar appreciates, imports into the U.S. become cheaper while our exports grow more expensive. A tariff on Chinese steel might limit the amount of steel coming into the U.S. from China, but it also makes U.S. exports more expensive and imports less expensive due to dollar appreciation. The upshot is that net exports don’t increase over the long run as a result of the change in exchange rates and the trade deficit remains. Thus, trade policy can create winners and losers among U.S. companies, but can’t reduce our trade deficit over the long-term – for that we’d need to increase savings.
However, trade policy can certainly impact our financial markets as well as the real economy. For example, the Chinese may decide to defend the 7.0 Yuan/dollar exchange rate to avoid capital fleeing Chinese shores for better returns elsewhere and to placate the U.S. as trade talks continue. The Chinese would have to sell some of their dollar reserves in order to buy the Yuan. Sales of dollar assets could include Treasuries, Corporate Bonds, and stocks, putting upward pressure on U.S. interest rates and downward pressure on the U.S. stock market. How big of an impact might Chinese selling have on the respective markets? We may find out in the coming months, depending on whether China decides to defend the 7.0 level or not.
Regards,
Christopher R Norwood, CFA
Chief Market Strategist