How to Find Profitable Stock Investments

Market Update
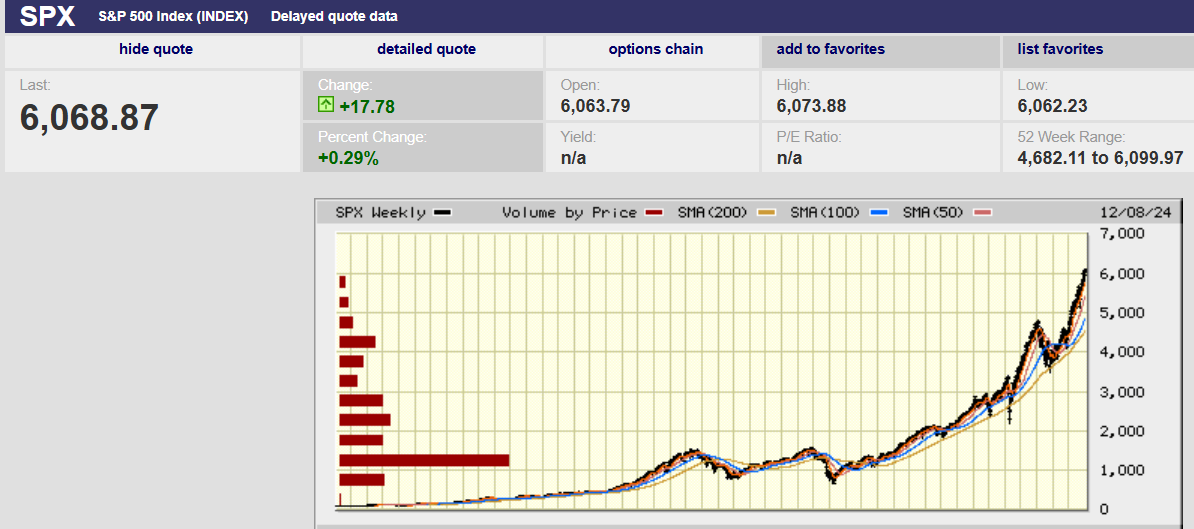
The S&P 500 rose 0.3% last week to finish at 4697.96. The index set a record Friday rising to 4718.5. The bull market is grinding higher, having gone 25 trading days without a 1% move in either direction. It is the longest stretch without a 1% move in two years. A slow grind higher is a classic sign of a strong market in which steady accumulation is taking place.
There is plenty to worry about though. The Federal Reserve will begin tightening monetary policy in December. The plan is to reduce bond-buying by $15 billion monthly, bringing QE to an end in 8 months. Some Fed members want to discuss reducing bond purchases faster. They believe interest rate hikes may need to happen sooner than planned. The Fed Funds Futures market is placing a 65% chance of the first hike happening in June 2022. Stock market risk is elevated whenever the Federal Reserve tightens monetary policy. Producer prices rising faster than consumer prices is also a concern. Either companies must accept reduced profit margins or pass costs through to consumers. In the latter case, consumers have less buying power when prices rise unless wages keep up.
A correction before year-end is unlikely. A correction early next year in response to Fed tightening is likely. A Fed decision to speed up the tightening timeline may trigger the pullback. It might be the return of Covid that acts as a catalyst. Oil is correcting now in part due to Austria implementing a lockdown. Germany is also locking down some regions in response to rising hospitalizations. It may be a forced unwinding by leveraged investors that sets off selling. Margin is near record highs. Call option buying points to speculation among retail investors. Regardless, Norwood Economics expects 2022 to be a flat to down year for the S&P 500. After three strong years, the S&P 500 could trade sideways for the next year or two while earnings catch up.
Economic Indicators
The Empire State manufacturing index jumped to 30.9 in November up from 19.8 in October. Retail sales were strong, gaining 1.7% in October after rising 0.8% in September. Industrial production was up 1.6% in October after falling 1.3% the prior month. Building permits increased to 1.65 million in October from 1.59 million. Building permits are a leading indicator of housing activity. The Philly Fed manufacturing index jumped to 39.0 in November from 23.8 in October. As well, the Leading Economic Indicator (LEI) rose 0.9% in October after rising 0.1% in September.
All in all, the economic data is pointing toward continued growth. The rebound in all the indicators last week makes it more likely that Q4 GDP growth will be better than Q3 growth. A recession continues to be unlikely before the second half of 2023. A 2024 recession is Norwood Economics’ current base forecast. It assumes the Federal Reserve will raise rates at least twice in 2022 and three to four times in 2023. It also assumes fiscal policy will tighten.
How to Find Profitable Stock Investments
First, you need to understand that stock is ownership in a company. One of my Butler University students told me a few weeks ago that stock is worthless. I pointed out that many stocks pay a dividend to the holder. He responded that stocks that didn’t pay dividends were worthless then. I explained that stock owners are entitled to a share of the profits of the business. I also explained that management had exactly three choices with how to use profits. It could pay out profits as dividends. It could use profits to buy back the company’s shares. Share buybacks increase the remaining owners’ stake in the company. It could keep earnings and use them to reinvest in the company. Reinvesting to grow the company grows earnings for owners.
My student also didn’t understand the relationship between earnings, earnings growth, dividends, and the stock price. Paying 10x earnings for a stock means you receive a 10% earnings yield. The earnings yield is the inverse of price-to-earnings. You are paying 10 dollars for a dollar of earnings. Earnings growth coupled with the dividend is your expected return. A stock growing earnings at 10% and paying a 3% dividend will return 13% annually, assuming the P/E ratio does not change. Value investors who buy earnings cheaply often get a return boost from P/E expansion. Conversely, growth investors who pay sky-high multiples for growth stocks often are penalized as the P/E multiple contracts. P/E multiples always contract for every stock as earnings growth slows. Earnings growth rates always slow as companies get bigger.
No one should buy a stock unless it will earn a risk-adjusted return above the market rate of return. Stock picking requires the investor to correctly judge that a stock is undervalued. A stock is undervalued if it subsequently returns more than the market on a risk-adjusted basis. Volatility is risk. Volatility is measured using beta with the beta of the market always being one. A stock that goes up 8% when the market rises 10% has a beta of 0.8. A stock with a beta of 0.8 that gains 9% when the market rises 10% is a stock worth buying. The extra 1% return is excess return and is known as alpha. Professional stock pickers are trying to add alpha or extra return. Again, if a stock picker can’t earn a higher risk-adjusted return than the overall market, they should not be buying individual stocks. They should buy the market instead.
Two final points:
Cryptocurrencies are not investments since they don’t have earnings. Instead, they are speculative instruments that rely on the greater fool theory. (Find a greater fool to buy the currency from you at a higher price than you paid.) Also, you should not be buying an individual stock if you don’t understand how to value the company and don’t understand risk-adjusted returns.
Regards,
Christopher R Norwood, CFA
Chief Market Strategist