Yet, the jobs market remains resilient

Market Update
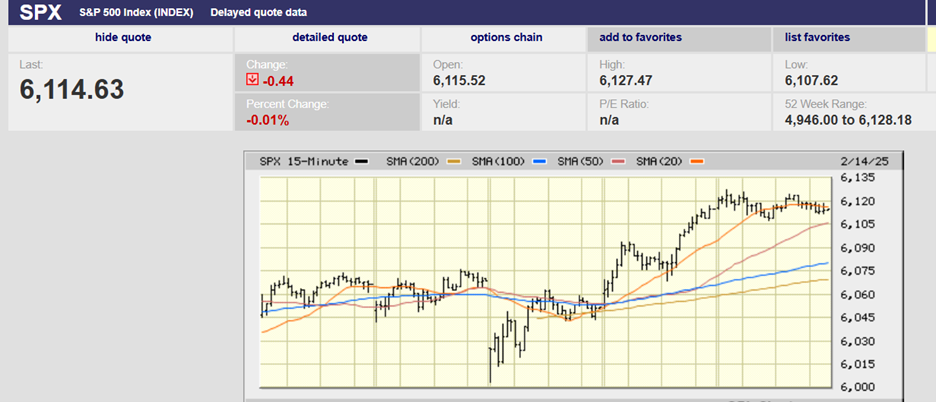
The S&P 500 rose 1.8% on the week as it broke decisively above resistance at 4,200. The index ended the week at 4,282.37. Next resistance is at 4,325.28. The Nasdaq and Dow rose 2.0% on the week. The Dow is in positive territory, up 2.0%, after spending most of the year in negative territory. The Nasdaq is up 27% on the year while the S&P is up 11.5%. The equal weight S&P index is up 1.8%. The S&P 500 Value Index is down 5.0% on the year.
The S&P gapped up at the open on Tuesday. The market was closed on Monday for Memorial Day. The gap up opening took the S&P to an early high of 4231.1. It was met with selling that sent the index to a low by mid-morning on Wednesday of 4,166.15. Thursday a rally took the S&P back above 4,200. The index hit a high Thursday afternoon of 4,232.43, exceeding the Tuesday high by 1.33 points. Traders would see the higher high as a short-term positive. The S&P gapped up 20 points at the open on Friday. The jobs report was credited. Strange given the strength of the report. A strong report doesn’t portend an end to the rate hike cycle.
Jobs growth rose by 339,000, well ahead of the 190,000 forecast. It was an increase from 294,000 the prior month. Another 93,000 jobs were added to the initial March and April numbers. It’s true the unemployment rate rose from 3.4% to 3.7% but that is still near 50-year lows. The unemployment rate won’t continue to move higher if jobs growth continues at its current pace. It is estimated that the U.S. needs to create around 70,000 jobs monthly to absorb new members of the workforce. As it is, job openings climbed back above 10 million. The April job openings number rose to 10.1 million from 9.7 million. The U.S. has a labor shortage. Wage growth will remain high as long as that shortage continues. Average hourly wages rose 4.3% year-over-year in May down from 4.4% the prior month. Wage growth above 4% isn’t compatible with an inflation rate of 2%. Wage growth was 4.2% annualized in the last three months.
Yet the market rallied on the jobs report. Or did it? The S&P 500 started to climb Wednesday afternoon. It moved steadily higher on Thursday and then vaulted higher on Friday after the jobs report. It is not a coincidence that the Federal Reserve was talking Wednesday afternoon about pausing in June. Federal Reserve Governor Jefferson gave a speech that raised the possibility of a June pause. Federal Reserve President Patrick Harker also suggested a pause is coming. It is likely that the market began rallying on Wednesday because of the Fed speakers. The jobs report showed enough weakness that it was considered safe to continue buying on Friday. The narrative of a Fed rate hike cycle ending soon is intact. Investors see a June pause as a necessary step before rate cuts can happen.
A lot is riding on the Fed pausing in June and not continuing rate hikes in July. Investors are buying based on the hope that the Fed will stop hiking rates. There is still hope also of cuts before year end, although that hope faded a bit last week. The CME FedWatch Tool has flipped to a 74.7% chance of a pause in June. Last week investors were assigning a 64% chance of a Fed rate hike. The sudden shift is due to the Fed speakers. Investors are assigning a 53.5% chance of a Fed rate hike in July and much reduced odds of a cut later this year. Cuts are unlikely with the economy growing at 2%, unemployment near 50-year lows, and inflation above 4%.
It should be an interesting second half. Fed policy is increasingly uncertain. A recession is still the consensus forecast. Earnings estimates have yet to take a recession into account, however. And the effects of the rapid rate hikes of last year are still working their way through the economy.
Economic Indicators
Home prices fell by 1.1% in March based on the Case-Shiller home price index. The forecast was for a rise of 0.4%. Falling home prices are bad for consumers. Equity in their home is the main source of wealth for most Americans. U.S. job openings rose to 10.1 million in April from 9.7 million the prior month. Economists had forecast 9.5 million job openings. Initial jobless claims were 232,000 last week, up from 230,000 the prior week. The job market continues to be tight, which will likely keep wage growth high.
The U.S. manufacturing PMI was 48.4 in May down from 48.5. The ISM manufacturing number fell to 46.9% in May from 47.1% in April. Numbers below 50 show contraction. The manufacturing economy continues to be in recession. The service economy continues to keep the entire economy out of recession.
Economic data last week showed an economy that continues to grow at around 2%. Financial conditions are looser than average. The Adjusted National Financial Conditions Index ANFCI) was unchanged last week at negative 0.33. A negative number means financial conditions are looser than average. Loose financial conditions are helping keep the economy (and the stock market) climbing. The economy is unlikely to fall into recession unless the Fed continues to tighten.
Liquidity and the Stock Market
The Treasury General Account (TGA) has provided liquidity for the stock market rally. The Treasury has been spending from the TGA for most of the year. The U.S. hit the former debt ceiling on 19 January and the Treasury announced a debt issuance suspension in response. Issuing debt absorbs liquidity. A suspension of issuance has the effect of injecting liquidity. The end of the debt ceiling impasse could be equal to a 0.25% rate hike, according to Barron’s. Liquidity will drain from the financial system as the Treasury sells billions of short-term bills to rebuild its cash balances. More financial condition tightening is coming from ongoing quantitative tightening. The Federal Reserve is shrinking its balance sheet by around $60 billion monthly. A shrinking balance sheet means a continuing decline in the money supply. A continuing decline in the money supply means upward pressure on interest rates.
Quantitative tightening (QT) and replenishing the TGA should impact the stock market. The Treasury’s cash management alone, “will flip from adding the equivalent of 3% of nominal gross domestic product over the past five months…to draining…nearly 10% in the next three months,” according to TS Lombard Chief U.S. Economist Steven Blitz. “This type of liquidity event always impacts equities,” Blitz wrote in a client note.
Add uncertainty about the impact of the Treasury's cash management to ongoing QT. Stir in uncertainty about the Federal Reserve’s next monetary policy moves. Shake well. Investors are left with a cocktail of factors that could result in a bumpy ride into year-end.
Regards,
Christopher R Norwood, CFA
Chief Market Strategist