FIXED INCOME ANNUITIES LOCK IN CASH FLOW IN RETIREMENT.
So why don’t more people use them?
FROM THE BLEACHERS, VOL. 17
MARKET UPDATE
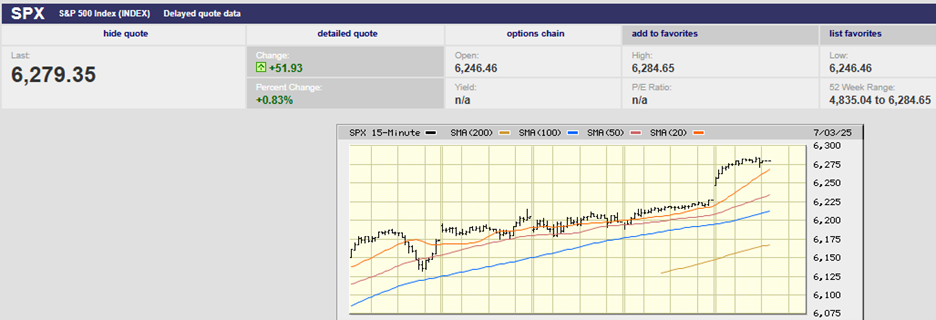
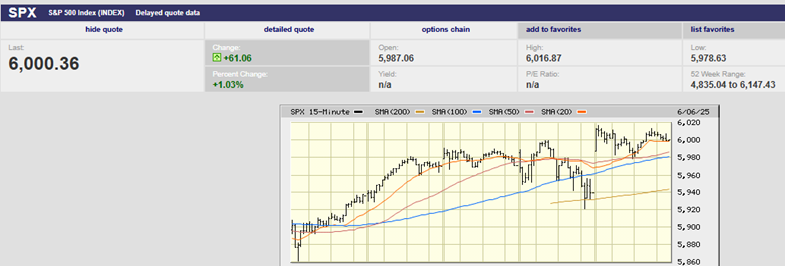
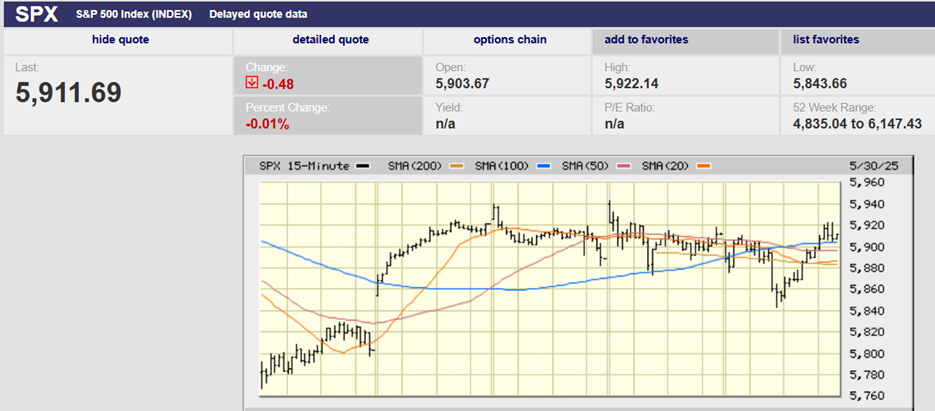
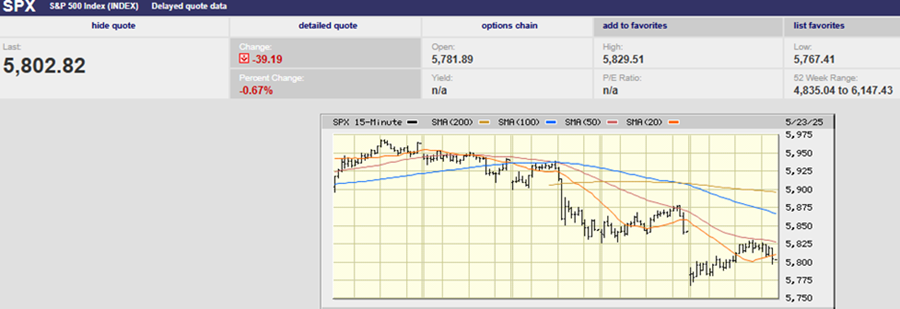
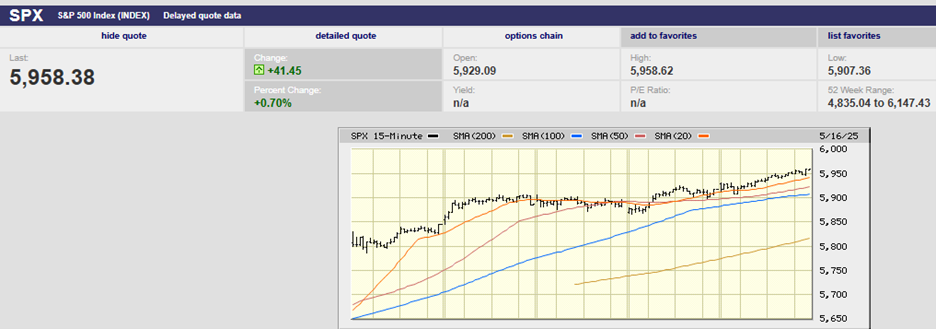
The S&P 500 set a record on a closing basis Friday, finishing the week at 2939.88. The index sits just below its all-time high of 2940.91. A close above the old high would be considered bullish by traders and many money managers alike and could well lead to an attempt to take out the big round 3,000 number just 2% above the current all-time high. Earnings reports continue to come in better than expected. About half of the S&P 500 companies have reported and earnings growth is averaging 2%, according to Barron’s, much better than the original forecast of a 3.8% decline. Furthermore, fully 80% of the companies that have reported have beat earnings estimates, a higher percentage than normal. Of course, companies have been meeting and beating much reduced estimates, as companies and analysts continue to play the earnings expectations game; lower estimates to the point that beating them becomes highly likely, declare the earnings beat a positive event, and hope investors believe it and buy.
There have been some notable misses however. 3M was hammered on Thursday, falling 13% after a poor earnings report. It was 3M’s worst single day loss in more than a decade. Likewise Intel dropped 9% on Friday after providing weak guidance for the rest of the year. 3M has broad exposure to both the U.S. and Asian economies while Intel still commands approximately 90% market share in microprocessors used for PCs, laptops, and servers. Big misses and weak guidance by big, economically important companies are often meaningful indicators of underlying economic activity.
On the other hand, Q1 GDP rose by 3.2%, much better than expected and a sharp improvement over the 2.2% growth in Q4. Morgan Stanley economists are expecting only 1.1% GDP growth in Q2 however, as Q1 GDP growth benefited from factors that aren’t sustainable and might even contribute to slower Q2 growth as those factors reverse. A sharp increase in inventory, for instance, added 0.7% to Q1 growth. Stripping out the increase in inventories drops Q1 GDP to 2.5%. Likewise, government spending increased by 2.4% annualized, reversing a 0.4% contraction in Q4 2018 spending. The government is on track to run a 2019 budget deficit of around $1 trillion or 5% of GDP, clearly an unsustainable number. Core spending, private domestic final sales, was only 1.3% in Q1 and is likely more indicative of what’s to come. It was the weakest private domestic final sales number in years.
The market always seems to surprise, so it’s entirely possible we’ll see a continued rise into year end, building on the already 17% gain in the S&P 500, but it’s less likely than a pullback at this point, given market valuations and slower underlying economic growth.
INVESTING – THE ANNUITIZATION PUZZLE
Accumulation annuities are typically expensive, restrictive, and undesirable if your goal is to create wealth for retirement. Fixed immediate payout annuities, on the other hand, are extremely useful and effective at helping solve your cash flow needs in retirement. Deferred fixed income annuities are even more useful at reducing or eliminating longevity risk. The puzzle is why more people don’t use them.
“Rational choice theory predicts that households will find annuities attractive at the onset of retirement because they address the risk of outliving one’s income,” write Benartzi, Previtero, and Thaler in their 2011 paper about the annuitization puzzle. Longevity risk is the primary problem solved by fixed immediate annuities. Longevity risk is the risk of outliving your assets. A man age 65 has a 50/50 chance of living to 82 and a woman to 85. One in ten men retiring at age 65 will live another 27 years while one in ten women will live another 30 years.
Immediate payout annuities are an insurance policy that allows you to increase consumption while reducing longevity risk. They work because people who die early are subsidizing those who live longer, which is also likely why many people aren’t keen on handing over a lump sum in exchange for lifetime cash flow. Loss aversion is well documented. We feel the pain of a loss around twice as much as any pleasure we receive from gains. The idea of dying prematurely and “losing” money on an immediate annuity as a result is a major turn off for people. The “loss” is the result of not collecting all of the payments that you would have received had you lived to the actuarially expected age. Of course, it’s no more a loss than if someone pays on a term life insurance policy for decades and then lets it lapse due to rising premiums and a declining need for life insurance.
Social security is the best immediate payout annuity available. Waiting until you turn 70 to capture the larger annuity is almost always the better choice. Social security is even inflation adjusted, which isn’t true of private annuities. Everyone then does have at least one immediate payout annuity in retirement as long as they are eligible for social security. The question is whether a second, private immediate payout annuity or deferred income annuity is appropriate, using a portion of your investable assets, to increase guaranteed cash flow to better cover necessary expenses in retirement. The answer is it depends. Too little liquid wealth makes it unwise to tie up a lump sum in a stream of future payments to you, while substantial liquid wealth makes it unnecessary to tie up a lump sum in a stream of payments to you. For the folks in between, however, buying an immediate or deferred income annuity with a portion of their liquid wealth can increase their ability to consume in retirement without increasing the risk of running out of money.
Regards,
Christopher R Norwood, CFA
Chief Market Strategist