Forget about the yield curve; Keep a diversified, low-cost portfolio

Market Update
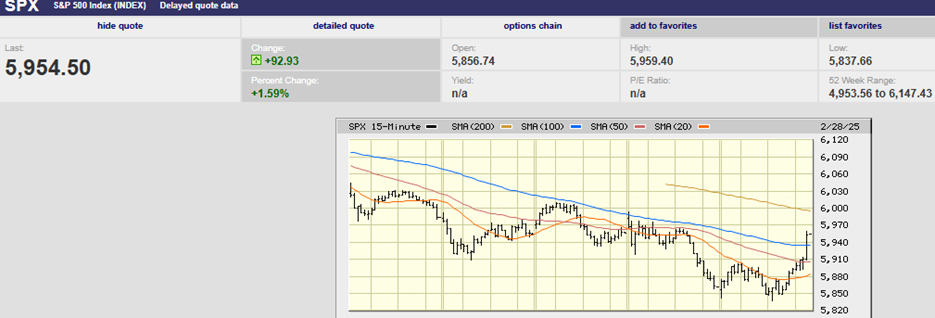
The S&P 500 rose 6.2% last week to finish at 4463.12. The index held the prior Tuesday’s low of 4157.87, bottoming at 4161.72 Monday. The S&P melted up the final four trading days of the week. The index finished near its high for the day and week on Friday. It also finished right below its 200-day moving average, taking out the 20-day and 50-day moving averages in the process. The 200-day represents resistance.
Last week felt like a short-covering rally. Short-covering rallies fall apart quickly. The S&P needs to clear the 200-day moving average this week or the selling will likely resume. The next few days are critical to how the index trades in the coming months.
The Nasdaq melted up 8.2% last week making it back to its 50-day moving average. The index is still well shy of its 200-day moving average. The Nasdaq traded in lockstep with the S&P 500. There were no major changes in the macroeconomic fundamentals to support either index’s move higher. As with the S&P 500, it felt like a short-covering rally. Unlike the S&P, the Nasdaq re-entered bear market territory last Monday, having fallen 22% peak to trough. We should see the Nasdaq lead the S&P 500 lower in the coming week if last week was nothing more than an oversold bounce.
The fundamental picture is as unclear as the short-term technical picture. GDP growth is forecast to slow. The Federal Reserve is forecasting 2.8% GDP growth in 2022, down from an earlier forecast of 4.0%. It is forecasting 2.2% growth in 2023 and 2.0% growth in 2024. The Conference Board sees GDP growth of 3.0% for 2022. It is forecasting GDP growth of 2.3% in 2023. The economy grew 6.9% in 2021.
Meanwhile, inflation, as measured by the CPI, is more than 8%. The Federal Reserve is forecasting inflation of 4.3% in 2022 falling to 2.7% in 2023 and 2.3% in 2024. The five-year breakeven inflation rate is 3.48%. It is the highest it has been since the measure was established in 2003. The five-year breakeven inflation rate is important because it expresses the bond market’s view of future inflation with real dollars on the line. The Federal Reserve is expecting the fed-funds rate to be at 1.9% by the end of 2022. It expects the fed-funds rate to have reached 2.8% by the end of 2023.
Rising rates and a slowing economy amidst decade’s high inflation is not a recipe for a rising stock market. Expect the stock market to trade sideways the rest of 2022, likely finishing down on the year.
Economic Indicators
One-year inflation expectations in February were 6.0%. Three-year inflation expectations are at 3.8%. Inflation expectations are important as they can influence actual inflation. For instance, there are indications that people are beginning to stockpile food, fearing higher prices, according to Barron’s. Hoarding is a classic behavior during inflationary times. The additional demand from hoarding leads to higher and more sustained inflation. Higher inflation expectations also impact wage demands which can create an inflationary spiral. Higher prices lead to higher wage demands which in turn leads to still higher prices.
The Empire state manufacturing index was minus 11.8 in March, a surprisingly weak reading. The forecast was for 5.5. It was the lowest reading since May 2020. Retail sales rose 0.3% in February down from 4.9% the prior month. The Philadelphia fed manufacturing index rose to 27.4 in March from 16 the prior month. The index of leading economic indicators rose 0.3% in February after falling 0.5% in January. All in all, the economic news last week was mixed and consistent with a slowing economy. Norwood Economics expects GDP growth to slow to 2.0% by year-end. It sees inflation slowing to between 4% and 5% over the next three to four quarters.
Rising Interest Rates and Bear Markets
The fear among investors is that Fed rate hikes will lead to a bear market. David Rosenberg of Rosenberg Research warns that Fed tightening cycles have had a 75% chance of triggering a recession, according to Barron’s. Recessions are accompanied bear markets. The odds favor a recession by the end of the rate tightening cycle accompanied by a bear market. However, tightening cycles can take years to play out. Stocks often rise during a tightening cycle.
Dow Jones Market Data recently analyzed the five most recent rate hike cycles to see how stocks did while rates were rising, according to Forbes. What Dow Jones Market Data found was that stocks usually continue to rise. The S&P 500 saw a median increase across all five cycles of 30%. The Nasdaq had a median gain of almost 27% and the Dow Jones Industrial Average a median gain of 17.4%.
Likewise, investors are increasingly pointing toward a flattening curve as a warning of losses to come. Perhaps. It is true that an inverted curve has proceeded every recession since 1955, with a recession following the inversion six to 24 months later. An inverted yield curve offered a false signal once, according to the Federal Reserve bank of San Francisco.
A flattening yield curve is not an inverted yield curve, however. Currently, the spread between the two-year and ten-year Treasury is 0.15%. The spread between the three-month and 10-year Treasury is 1.72%. The latter spread is important because it is the 3-month/10-year spread that the Federal Reserve believes is more predictive. It is the spread it uses in its models to forecast the probability of a recession. The 3-month/10-year spread is not particularly flat.
A recession is not looming, at least not according to the yield curve. Neither the two/ten curve nor the 3mth/ten curve are inverted. And the lag between an inversion and recession is between six and 24 months. Investors should not change allocations based on the steepness of the yield curve. Trying to predict recessions and bear markets is not likely to improve your investing results. Instead, focus on an appropriate portfolio allocation based on your financial goals. Build a diversified, low-cost portfolio most likely to help you achieve a successful retirement. Leave the guessing games to the so-called pundits.
Regards,
Christopher R Norwood, CFA
Chief Market Strategist